PostgreSQL
The PostgreSQL data source connector connects Prisma ORM to a PostgreSQL database server.
By default, the PostgreSQL connector contains a database driver responsible for connecting to your database. You can use a driver adapter (Preview) to connect to your database using a JavaScript database driver from Prisma Client.
Need a Postgres instance yesterday?
With Prisma Postgres you can get a database running on bare-metal in three clicks. Connection pooling, query caching, and automated backups are all included. to get started today.
Want any even faster way to get started with Prisma Postgres? Just run npx prisma init --db in your terminal. 🚀
Example
To connect to a PostgreSQL database server, you need to configure a datasource block in your Prisma schema:
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
The fields passed to the datasource block are:
provider: Specifies thepostgresqldata source connector.url: Specifies the connection URL for the PostgreSQL database server. In this case, an environment variable is used to provide the connection URL.
Using the node-postgres driver
As of v5.4.0, you can use Prisma ORM with database drivers from the JavaScript ecosystem (instead of using Prisma ORM's built-in drivers). You can do this by using a driver adapter.
For PostgreSQL, node-postgres (pg) is one of the most popular drivers in the JavaScript ecosystem. It can be used with any PostgreSQL database that's accessed via TCP.
This section explains how you can use it with Prisma ORM and the @prisma/adapter-pg driver adapter.
1. Install the dependencies
First, install Prisma ORM's driver adapter for pg:
npm install @prisma/adapter-pg
2. Instantiate Prisma Client using the driver adapter
Now, when you instantiate Prisma Client, you need to pass an instance of Prisma ORM's driver adapter to the PrismaClient constructor:
import { PrismaPg } from '@prisma/adapter-pg'
import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client'
const connectionString = `${process.env.DATABASE_URL}`
const adapter = new PrismaPg({ connectionString });
const prisma = new PrismaClient({ adapter });
Notice that this code requires the DATABASE_URL environment variable to be set to your PostgreSQL connection string. You can learn more about the connection string below.
Notes
Specifying a PostgreSQL schema
You can specify a PostgreSQL schema by passing in the schema option when instantiating PrismaPg:
const adapter = new PrismaPg(
{ connectionString },
{ schema: 'myPostgresSchema' }
)
Connection details
Connection URL
Prisma ORM follows the connection URL format specified by PostgreSQL's official guidelines, but does not support all arguments and includes additional arguments such as schema. Here's an overview of the components needed for a PostgreSQL connection URL:
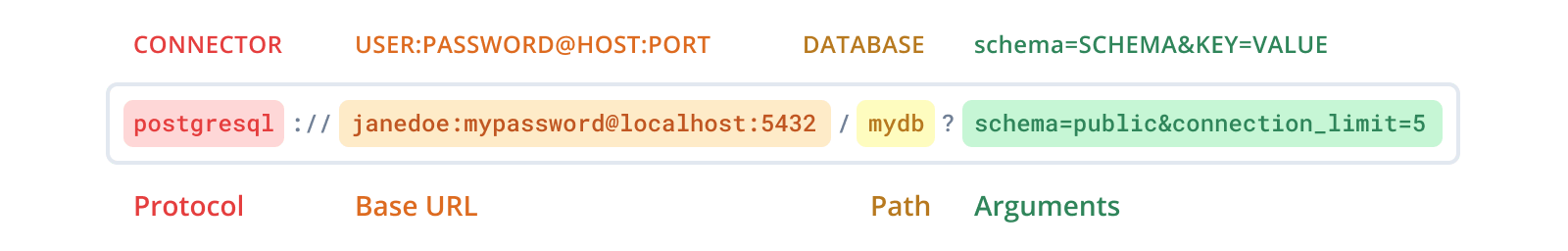
Base URL and path
Here is an example of the structure of the base URL and the path using placeholder values in uppercase letters:
postgresql://USER:PASSWORD@HOST:PORT/DATABASE
The following components make up the base URL of your database, they are always required:
| Name | Placeholder | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Host | HOST | IP address/domain of your database server, e.g. localhost |
| Port | PORT | Port on which your database server is running, e.g. 5432 |
| User | USER | Name of your database user, e.g. janedoe |
| Password | PASSWORD | Password for your database user |
| Database | DATABASE | Name of the database you want to use, e.g. mydb |
You must percentage-encode special characters.
Arguments
A connection URL can also take arguments. Here is the same example from above with placeholder values in uppercase letters for three arguments:
postgresql://USER:PASSWORD@HOST:PORT/DATABASE?KEY1=VALUE&KEY2=VALUE&KEY3=VALUE
The following arguments can be used:
| Argument name | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
schema | Yes | public | Name of the schema you want to use, e.g. myschema |
connection_limit | No | num_cpus * 2 + 1 | Maximum size of the connection pool |
connect_timeout | No | 5 | Maximum number of seconds to wait for a new connection to be opened, 0 means no timeout |
pool_timeout | No | 10 | Maximum number of seconds to wait for a new connection from the pool, 0 means no timeout |
sslmode | No | prefer | Configures whether to use TLS. Possible values: prefer, disable, require |
sslcert | No | Path of the server certificate. Certificate paths are resolved relative to the ./prisma folder | |
sslrootcert | No | Path of the root certificate. Certificate paths are resolved relative to the ./prisma folder | |
sslidentity | No | Path to the PKCS12 certificate | |
sslpassword | No | Password that was used to secure the PKCS12 file | |
sslaccept | No | accept_invalid_certs | Configures whether to check for missing values in the certificate. Possible values: accept_invalid_certs, strict |
host | No | Points to a directory that contains a socket to be used for the connection | |
socket_timeout | No | Maximum number of seconds to wait until a single query terminates | |
pgbouncer | No | false | Configure the Engine to enable PgBouncer compatibility mode |
statement_cache_size | No | 100 | Since 2.1.0: Specifies the number of prepared statements cached per connection |
application_name | No | Since 3.3.0: Specifies a value for the application_name configuration parameter | |
channel_binding | No | prefer | Since 4.8.0: Specifies a value for the channel_binding configuration parameter |
options | No | Since 3.8.0: Specifies command line options to send to the server at connection start |
As an example, if you want to connect to a schema called myschema, set the connection pool size to 5 and configure a timeout for queries of 3 seconds. You can use the following arguments:
postgresql://USER:PASSWORD@HOST:PORT/DATABASE?schema=myschema&connection_limit=5&socket_timeout=3
Configuring an SSL connection
You can add various parameters to the connection URL if your database server uses SSL. Here's an overview of the possible parameters:
sslmode=(disable|prefer|require):prefer(default): Prefer TLS if possible, accept plain text connections.disable: Do not use TLS.require: Require TLS or fail if not possible.
sslcert=<PATH>: Path to the server certificate. This is the root certificate used by the database server to sign the client certificate. You need to provide this if the certificate doesn't exist in the trusted certificate store of your system. For Google Cloud this likely isserver-ca.pem. Certificate paths are resolved relative to the./prisma foldersslidentity=<PATH>: Path to the PKCS12 certificate database created from client cert and key. This is the SSL identity file in PKCS12 format which you will generate using the client key and client certificate. It combines these two files in a single file and secures them via a password (see next parameter). You can create this file using your client key and client certificate by using the following command (usingopenssl):openssl pkcs12 -export -out client-identity.p12 -inkey client-key.pem -in client-cert.pemsslpassword=<PASSWORD>: Password that was used to secure the PKCS12 file. Theopensslcommand listed in the previous step will ask for a password while creating the PKCS12 file, you will need to provide that same exact password here.sslaccept=(strict|accept_invalid_certs):strict: Any missing value in the certificate will lead to an error. For Google Cloud, especially if the database doesn't have a domain name, the certificate might miss the domain/IP address, causing an error when connecting.accept_invalid_certs(default): Bypass this check. Be aware of the security consequences of this setting.
Your database connection URL will look similar to this:
postgresql://USER:PASSWORD@HOST:PORT/DATABASE?sslidentity=client-identity.p12&sslpassword=mypassword&sslcert=rootca.cert
Connecting via sockets
To connect to your PostgreSQL database via sockets, you must add a host field as a query parameter to the connection URL (instead of setting it as the host part of the URI).
The value of this parameter then must point to the directory that contains the socket, e.g.: postgresql://USER:PASSWORD@localhost/database?host=/var/run/postgresql/
Note that localhost is required, the value itself is ignored and can be anything.
Note: You can find additional context in this GitHub issue.
Type mapping between PostgreSQL and Prisma schema
These two tables show the type mapping between PostgreSQL and Prisma schema. First how Prisma ORM scalar types are translated into PostgreSQL database column types, and then how PostgreSQL database column types relate to Prisma ORM scalar and native types.
Alternatively, see Prisma schema reference for type mappings organized by Prisma type.
Mapping between Prisma ORM scalar types and PostgreSQL database column types
The PostgreSQL connector maps the scalar types from the Prisma ORM data model as follows to database column types:
| Prisma ORM | PostgreSQL |
|---|---|
String | text |
Boolean | boolean |
Int | integer |
BigInt | bigint |
Float | double precision |
Decimal | decimal(65,30) |
DateTime | timestamp(3) |
Json | jsonb |
Bytes | bytea |
Mapping between PostgreSQL database column types to Prisma ORM scalar and native types
- When introspecting a PostgreSQL database, the database types are mapped to Prisma ORM types according to the following table.
- When creating a migration or prototyping your schema the table is also used - in the other direction.
| PostgreSQL (Type | Aliases) | Supported | Prisma ORM | Native database type attribute | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
bigint | int8 | ✔️ | BigInt | @db.BigInt* | *Default mapping for BigInt - no type attribute added to schema. |
boolean | bool | ✔️ | Bool | @db.Boolean* | *Default mapping for Bool - no type attribute added to schema. |
timestamp with time zone | timestamptz | ✔️ | DateTime | @db.Timestamptz(x) | |
time without time zone | time | ✔️ | DateTime | @db.Time(x) | |
time with time zone | timetz | ✔️ | DateTime | @db.Timetz(x) | |
numeric(p,s) | decimal(p,s) | ✔️ | Decimal | @db.Decimal(x, y) | |
real | float, float4 | ✔️ | Float | @db.Real | |
double precision | float8 | ✔️ | Float | @db.DoublePrecision* | *Default mapping for Float - no type attribute added to schema. |
smallint | int2 | ✔️ | Int | @db.SmallInt | |
integer | int, int4 | ✔️ | Int | @db.Int* | *Default mapping for Int - no type attribute added to schema. |
smallserial | serial2 | ✔️ | Int | @db.SmallInt @default(autoincrement()) | |
serial | serial4 | ✔️ | Int | @db.Int @default(autoincrement()) | |
bigserial | serial8 | ✔️ | Int | @db.BigInt @default(autoincrement() | |
character(n) | char(n) | ✔️ | String | @db.Char(x) | |
character varying(n) | varchar(n) | ✔️ | String | @db.VarChar(x) | |
money | ✔️ | Decimal | @db.Money | |
text | ✔️ | String | @db.Text* | *Default mapping for String - no type attribute added to schema. |
timestamp | ✔️ | DateTime | @db.TimeStamp* | *Default mapping for DateTime - no type attribute added to schema. |
date | ✔️ | DateTime | @db.Date | |
enum | ✔️ | Enum | N/A | |
inet | ✔️ | String | @db.Inet | |
bit(n) | ✔️ | String | @Bit(x) | |
bit varying(n) | ✔️ | String | @VarBit | |
oid | ✔️ | Int | @db.Oid | |
uuid | ✔️ | String | @db.Uuid | |
json | ✔️ | Json | @db.Json | |
jsonb | ✔️ | Json | @db.JsonB* | *Default mapping for Json - no type attribute added to schema. |
bytea | ✔️ | Bytes | @db.ByteA* | *Default mapping for Bytes - no type attribute added to schema. |
xml | ✔️ | String | @db.Xml | |
| Array types | ✔️ | [] | ||
citext | ✔️* | String | @db.Citext | * Only available if Citext extension is enabled. |
interval | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
cidr | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
macaddr | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
tsvector | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
tsquery | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
int4range | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
int8range | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
numrange | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
tsrange | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
tstzrange | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
daterange | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
point | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
line | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
lseg | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
box | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
path | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
polygon | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
circle | Not yet | Unsupported | ||
| Composite types | Not yet | n/a | ||
| Domain types | Not yet | n/a |
Introspection adds native database types that are not yet supported as Unsupported fields:
model Device {
id Int @id @default(autoincrement())
name String
data Unsupported("circle")
}
Prepared statement caching
A prepared statement is a feature that can be used to optimize performance. A prepared statement is parsed, compiled, and optimized only once and then can be executed directly multiple times without the overhead of parsing the query again.
By caching prepared statements, Prisma Client's query engine does not repeatedly compile the same query which reduces database CPU usage and query latency.
For example, here is the generated SQL for two different queries made by Prisma Client:
SELECT * FROM user WHERE name = "John";
SELECT * FROM user WHERE name = "Brenda";
The two queries after parameterization will be the same, and the second query can skip the preparing step, saving database CPU and one extra roundtrip to the database. Query after parameterization:
SELECT * FROM user WHERE name = $1
Every database connection maintained by Prisma Client has a separate cache for storing prepared statements. The size of this cache can be tweaked with the statement_cache_size parameter in the connection string. By default, Prisma Client caches 100 statements per connection.
Due to the nature of pgBouncer, if the pgbouncer parameter is set to true, the prepared statement cache is automatically disabled for that connection.